Needle Thoracostomy Procedure
- 1. Universal Precautions
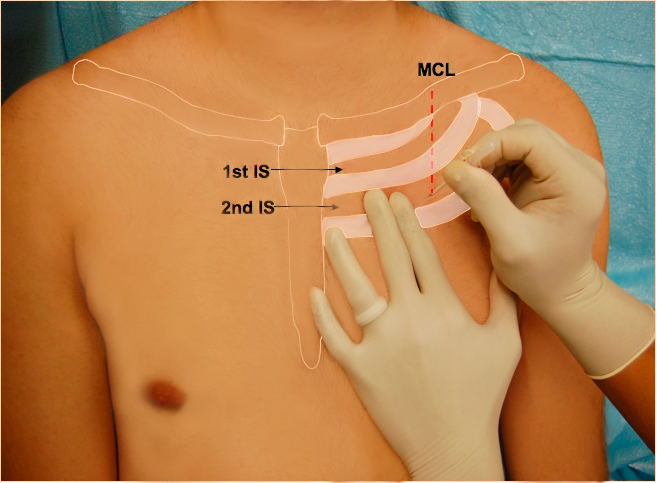
- 2. Identify anatomical landmarks: Locate the 2nd intercostal space between the 2nd and 3rd ribs at the midclavicular line
- 3. Choose an appropriate size and length catheter (infants: 22 gauge, toddlers/preschoolers: 20 gauge, school-aged: 18 gauge, 14-16 gauge in adolescents)
- 4. Prep the insertion site with betadine or other approved cleansing agent
- 5. Place needle tip in the 2nd intercostal space above 3rd rib (to avoid intercostal artery and vein) in the midclavicular line
- 5. Insert the catheter until a rush of air is heard or felt
- 6. A flutter valve may be used (depending on local protocol)
- 7. Secure the catheter to the chest wall to prevent dislodgement
- 8. Follow with placement of a thoracostomy tube as soon as able