Indications of Child Abuse
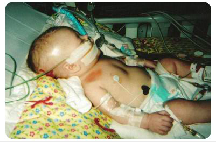
- Look for signs of head injury, lethargy, irritability, altered mental status, seizure, unequal pupils.
- Petechiae to the arms or chest (hand grip signs) where the child was held.
- Located on soft tissue, e.g., neck, buttocks, back, thighs and genitalia.
- Facial bruises from punches or slaps.
- Bruises in non-ambulatory children, e.g., < 9 months or physical disabled.
- Look for "sparing" - unburned areas, e.g., creases of knees, toes, palms where the child withdraws or buttocks where child was pushed firmly against tub floor.
- Non-ambultory children, e.g., < 9 months old or physically disabled.
Factors for identifying abuse include: an explanation of events that is inconsistent with the injury; burn(s) to the buttocks, sacrum, ankles / soles, or wrists / palms indicative of immersion in hot liquid; injuries of different ages, such as fractures, healed burns or bruises; a delay in seeking medical attention; and when caretakers appear angry or resentful toward the child or each other. Here are some common injury patterns that may be seen in abuse.