Spinal Motion Restriction
- Should be done as soon as possible if cervical spine (C-spine) injury is suspected.
- Altered level of consciousness.
- High suspicion mechanism of injury (ejection, fall from height, etc.).
- Signs of head or neck trauma.
- Neurologic abnormalities (e.g., weakness, numbness).
- Spinal stabilization with motion restriction should be maintained throughout the assessment.
- Maintain the head and neck in a neutral position.
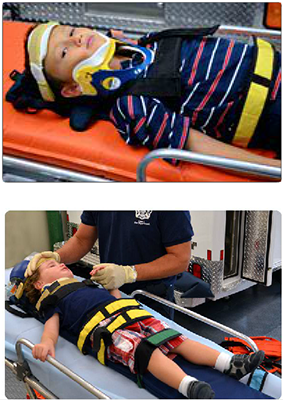
The primary assessment should be conducted while maintaining spinal in-line stabilization with patients who may have a cervical spine injury. Conditions where a spinal injury should be suspected include patients with altered level of consciousness; high suspicion of mechanism of injury such as ejection from a motor vehicle, fall from height or pedestrian struck; signs of head or neck trauma; or neurologic abnormalities (e.g., weakness, numbness).
Spinal stabilization with motion restriction should be maintained throughout the assessment by maintaining the head in a neutral position.