Program Progress:
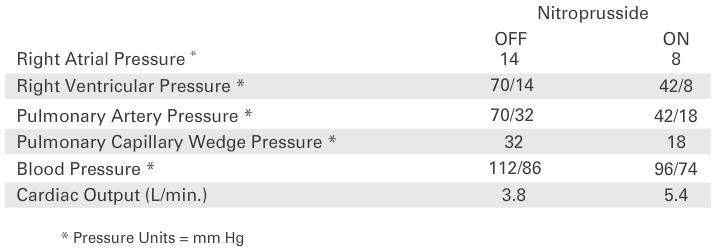
IV nitroprusside Administered and Hemodynamic Results
Emergency medical therapy with intravenous nitroprusside is commonly used in the treatment of acute heart failure when the blood pressure is adequate to maintain cerebral, coronary and renal perfusion. It is an effective venous and arteriolar vasodilator and acts by reducing both preload and afterload. The latter effect decreases both systemic and pulmonary vascular resistance. Its onset of action is rapid and readily reversible and its hemodynamic effect predictable. These hemodynamic changes are effective in augmenting forward cardiac output and decreasing symptoms. An additional immediate therapy is intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation. A pulmonary artery balloon flotation catheter was inserted to precisely determine our patient's hemodynamic status and response to nitroprusside. This table demonstrates the nitroprusside therapy lowered the pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, as well as all of the other pressure measurements and improved cardiac output.